Typical products
Typical partners
Frequently asked questions
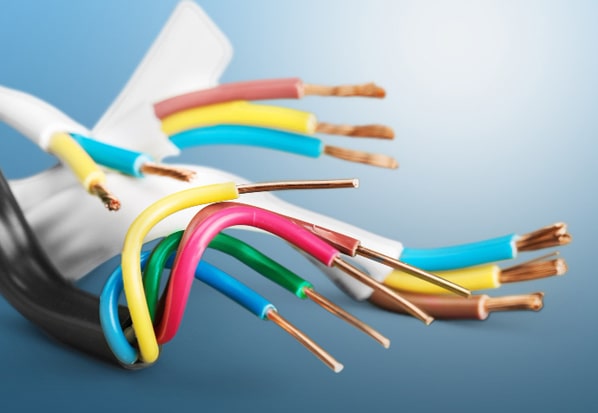
Electric cables are defined as wires or cables capable of conducting electricity. Electric wires are usually residential wires, transmitting voltages below 1000V (1kV) and have 1 conductor, while electric cables are usually multi-conductor types (2 cores or more), often used to load voltages of 1kV or more. .
There are many ways to classify electric cables :
- By voltage level : Residential electric wire (load voltage up to 750V), low voltage cable (load voltage 0.6/1kV), medium voltage cable (load voltage from 1kV to 36kV), high voltage cable (load voltage from 36kV or more).
- According to installation method : Suspended electric cables (overhead, placed in cable trays) are collectively called suspended cables, underground cables (placed underground – underground or underwater – submarine).
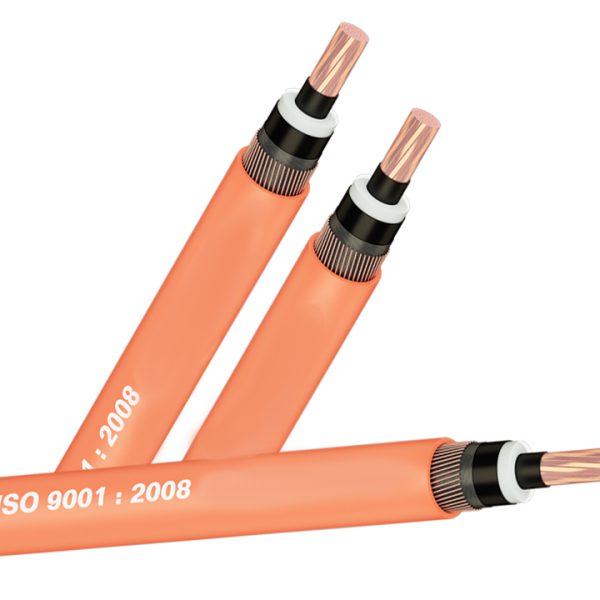
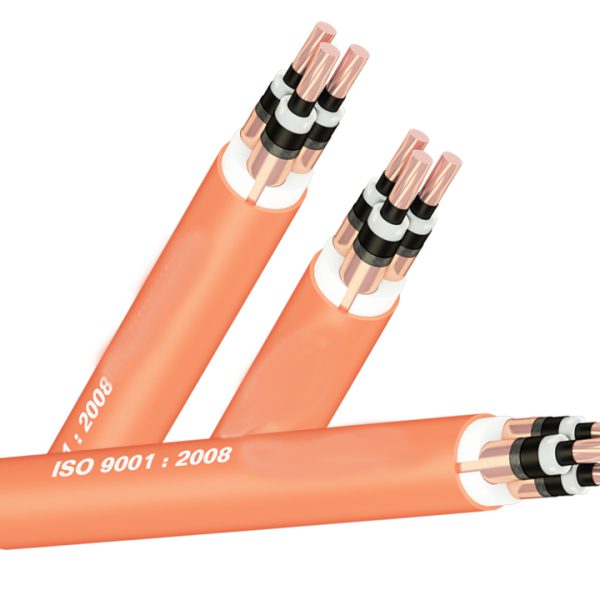
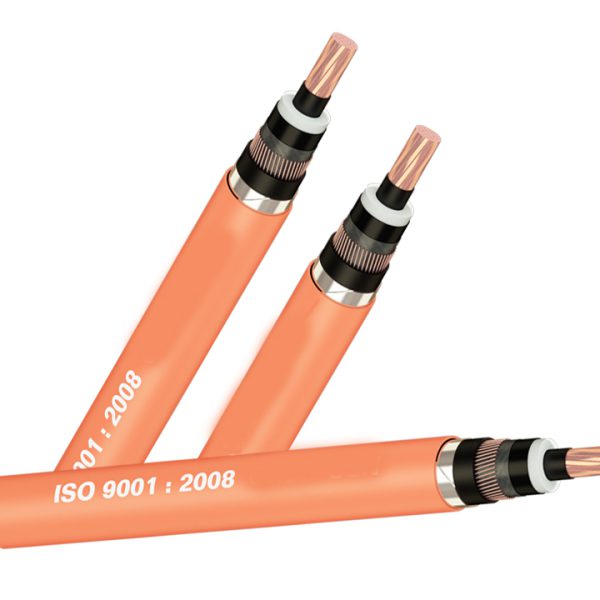
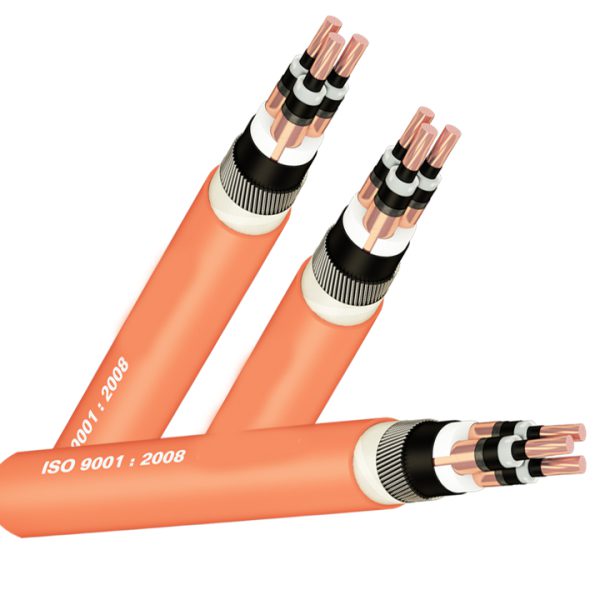
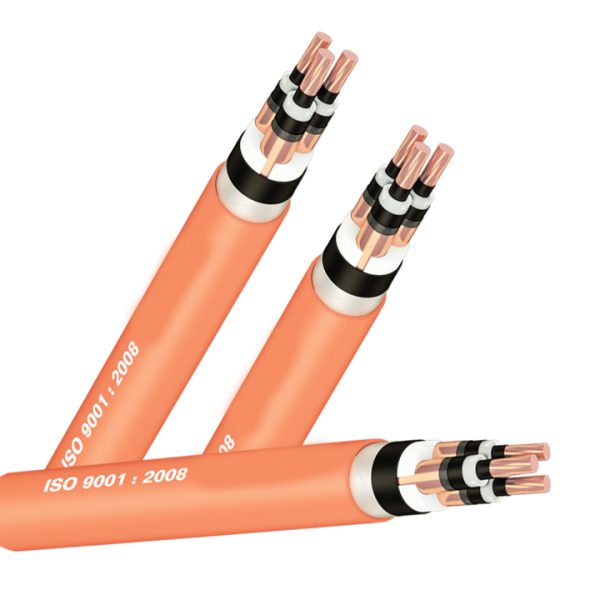
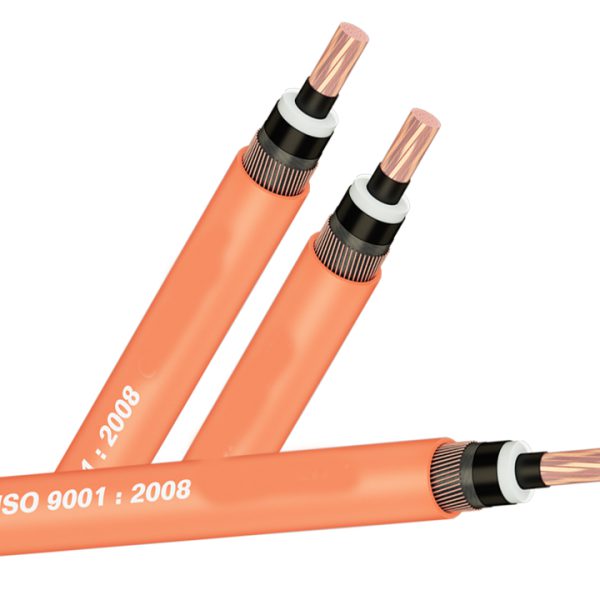
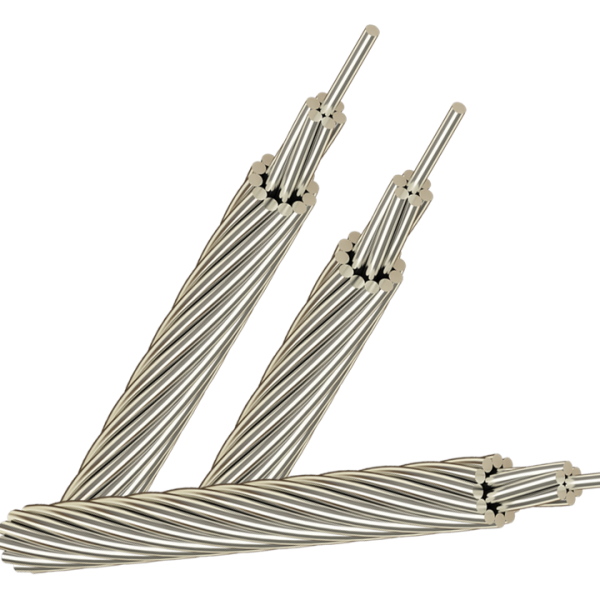
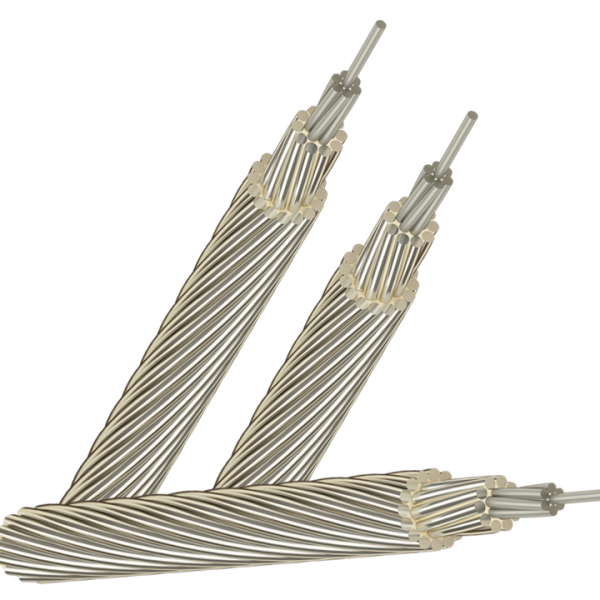
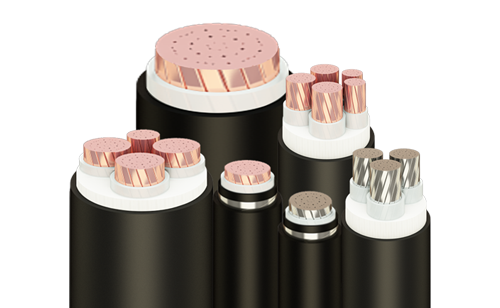
- By structure : Single-conductor cable, multi-conductor cable, PVC insulated wire, XLPE insulated wire, bare cable, fireproof cable, shielded cable, unshielded cable, armored cable, unarmored cable …
Wires and cables need to comply with standards. Standards are regulated by Country such as TCVN (Vietnam), BS (UK), SS (Singapore), NEC (USA) or International standards (IEC).
TCVN complies with IEC international standards. Specifically, the most commonly applied standards related to electric wires and cables are: TCVN 6447:1998, TCVN 6610:2014, TCVN 6612:2007, TCVN 5064:1994, TCVN 5935:2013, IEC 60331, IEC 60332, BS 6387, BS 7835…
The meaning of the abbreviated symbols on the cable is as follows:
- 0.6/1 (1.2) kV: Nominal voltage 0.6 – 1kV, maximum 1.2kV;
- ABC (Aerial Bundled cable): Twisted cable;
- C or Cu: Copper;
- A or Al: Aluminum;
- AS: Aluminum steel core;
- X or XLPE: cross-linked polyethylene resin XLPE;
- V or PVC: thermoplastic PVC;
- DATA (double aluminum tape armored): Stainless steel tape layer;
- DSTA (double steel tape armored): Aluminum tape layer;
- SWA (Steel wire amoured): Steel wire armor;
- AWA (Aluminum wire amoured): Aluminum wire armor;
- 3×70: 3 conductors, each conductor has a cross section of 70mm2;
- E: Ground wire.
For example: Cable with symbol CXV 0.6/1 (1.2)kV 4×70: Copper conductor cable, XLPE insulation, PVC sheath, nominal voltage 0.6/1 (1.2)kV, 4-conductor type, details The area of each conductor is 70mm2.
The cable insulation material used is based on the load voltage. As follows:
- Low voltage/medium voltage (up to 35kV) : EPR/HEPR rubber; PVC, PE, XLPE, MDPE, LDPE, HDPE, insulated with Mass-Impregnated paper…
- High voltage (over 35kV) : Polypropylene, liquid insulation such as oil (HPFF), gas insulation such as SF6, Nitrogen (HPGF), self-contained oil pipe insulation (SCFF), XLPE insulation or natural air insulation (overhead lines).
- Special types of cables : Mineral insulation, PTFE (medical field), LSZH insulation (fire resistant cable)…
The metal sheath inside the cable protects the conductor and insulation layer of the cable from agents such as: Moisture, gas, acids or alkalis, hydrocarbons and petrochemical compounds… This is the sheath. in, mainly used for submarine cables. The casing is mainly lead, but is now gradually being replaced by HDPE plastic and other compounds.